How Mind Mapping Helps Students with Learning Disabilities Succeed
Learning disabilities affect millions of students worldwide, creating unique challenges in processing and retaining information. Traditional linear note-taking methods may not effectively support diverse learning styles or cognitive needs. Mind mapping offers a powerful visual and organizational tool that helps transform how learners with dyslexia, ADHD, dyscalculia, dysgraphia, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and other learning differences approach studying and problem-solving.
Curious how visual learning can support every learner?
Learning Differences vs. Learning Difficulties vs. Learning Disabilities: Understanding the Distinction
The terms are often used interchangeably, but they carry important distinctions. Learning differences refer to the natural variations in how people learn at different speeds and in different ways. Learning difficulties are external factors like poor teaching or lack of school attendance that may affect learning ability. Learning disabilities, however, are specific neurological conditions that don't respond well to typical educational interventions and require adapted learning strategies.
Current Situation of Students with Disabilities: Understanding the Data
The landscape of disability education has shifted dramatically over the past decade. According to recent statistics, approximately one in five students in the United States has a learning disability, affecting their academic performance and confidence. These challenges extend beyond the classroom, impacting self-esteem, career prospects, and long-term success.
Students with learning disabilities often experience frustration when traditional teaching methods don't align with how their brains process information. Many are labeled as "lazy" or "unmotivated" when, in reality, they're using ineffective learning strategies designed for neurotypical minds. The gap between potential and performance creates a devastating cycle of discouragement.
However, the tide is turning. Schools and educators increasingly recognize that learning disabilities require tailored learning strategies, not remedial approaches. Visual learning has emerged as a game-changer, offering students alternative pathways to understanding complex information. Mind mapping, in particular, has shown remarkable results in helping students with various disabilities achieve academic success.
What is Mind Mapping?
Mind mapping is a visual technique that organizes information non-linearly around a central concept. Unlike traditional outlines, mind maps use branches radiating from a core idea to represent related topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Each branch incorporates colors, symbols, and images, creating a memorable structure that mirrors the brain's natural way of making connections, improving comprehension and retention.
This approach not only enhances creative thinking but also helps learners visualize relationships between ideas, making complex subjects easier to understand. Whether used for studying, planning, or brainstorming, mind mapping turns information into an interactive and engaging experience.
Why Mind Mapping Benefits Students with Learning Disabilities
Engages Multiple Learning Modalities
Mind maps naturally engage multiple learning modalities, making them highly effective for diverse learners. By integrating visual elements, spatial relationships, and strategic color coding, they appeal to visual learners who process information best through images and patterns. The hands-on process of drawing, arranging, and organizing information supports kinesthetic learners who need physical engagement to reinforce understanding. Additionally, mind maps reduce reliance on dense text, which enhances accessibility particularly for students with dyslexia who may struggle with traditional reading-heavy materials. This multi-modal approach ensures that students can access and process information through their preferred learning channels.
Reduces Cognitive Overload
Mind maps are particularly effective at reducing cognitive overload by breaking complex information into manageable, focused chunks that are easier to digest and understand. This chunking approach allows learners to process one concept at a time without feeling overwhelmed, which significantly reduces anxiety often associated with tackling large amounts of information. The visual structure naturally encourages learners to see and understand the relationships between ideas, creating meaningful connections rather than trying to memorize isolated facts. By externalizing information onto the map, students free up valuable mental resources, making learning feel less taxing and more achievable.
Enhances Organization and Executive Function
Mind maps significantly enhance organization and executive function by providing a clear visual hierarchy that distinguishes main ideas from supporting details. This structured approach helps students see the big picture while understanding how smaller pieces fit together, which is particularly valuable for those who struggle with organizational skills. The process of creating and using mind maps supports metacognitive skills by encouraging learners to think about how they think, actively organizing their thoughts in a deliberate and visible way. Over time, regular use of mind mapping strengthens executive functioning abilities, helping students develop better planning strategies, maintain focus on tasks, and manage their learning process more independently and effectively.
Struggling to organize ideas while studying?
Mind Mapping Strategies for Specific Learning Disabilities
1. Dyslexia
For students with dyslexia, mind maps offer a powerful alternative to traditional text-heavy learning materials by prioritizing images and spatial layouts. By incorporating icons, pictures, and visual symbols throughout the map, the reading demands are significantly reduced, allowing students to process information through their visual strengths rather than struggling with dense text. Color-coding serves as an effective organizational tool, helping to differentiate between topics and create memorable visual associations. When combined with text-to-speech technology, mind maps become a multi-sensory learning experience that reinforces comprehension through both visual and auditory channels, making information more accessible and easier to retain.
2. ADHD
Mind mapping proves particularly effective for students with ADHD by leveraging visual stimulation and active participation to maintain focus and engagement. The branching structure naturally breaks complex tasks into smaller, manageable segments, preventing the overwhelming feeling that often accompanies large assignments or dense information. The flexible, non-linear layout supports the rapid idea generation that many ADHD learners excel at, allowing thoughts to flow freely without the constraints of traditional note-taking formats. Digital mind mapping tools that incorporate gamification elements such as rewards, progress tracking, and interactive features can further enhance motivation and sustain attention throughout the learning process.
3. Dyscalculia
Students with dyscalculia benefit immensely from mind mapping's ability to transform abstract mathematical concepts into visual, concrete representations. By using number lines, charts, diagrams, and strategic color-coding, mathematical relationships and operations become tangible and easier to grasp. Mind maps are especially valuable for organizing word problems visually, breaking them down into clear, sequential steps that reduce confusion and anxiety. This visual approach significantly reduces cognitive load by externalizing the problem-solving process, allowing students to see the relationships between numbers and concepts rather than holding everything in working memory.
Curious how AI can turn notes into clear visuals?
4. Dysgraphia
For learners with dysgraphia, mind mapping minimizes the physical act of writing, often a significant barrier by emphasizing symbols, simple sketches, and abbreviations over lengthy written explanations. Digital mind mapping tools paired with voice-to-text technology allow students to bypass handwriting challenges entirely while still capturing their ideas effectively. The focus shifts from textual content to visual representation, enabling students to express their understanding and organize their thoughts without the frustration and fatigue that traditional writing tasks impose.
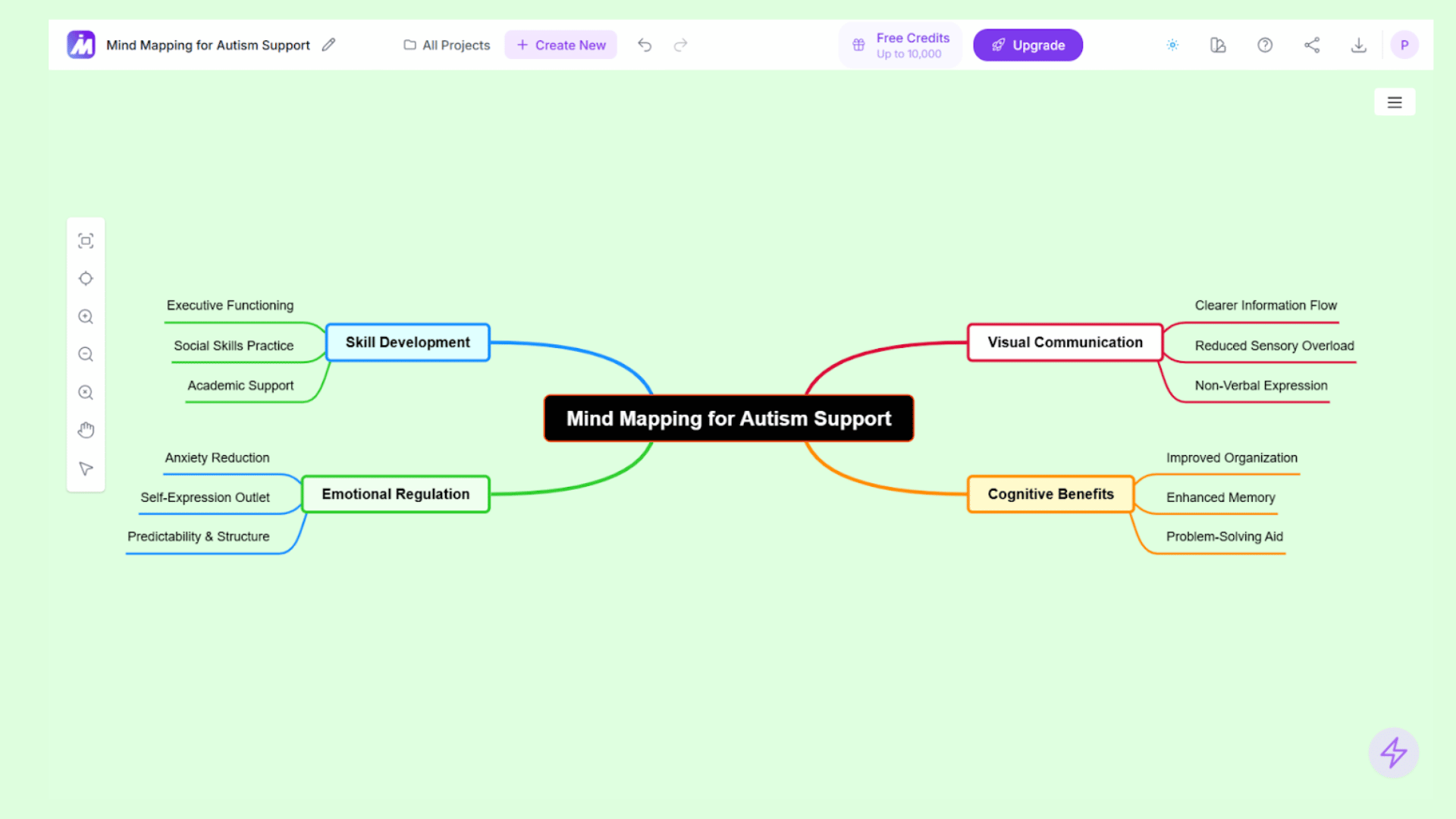
5. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Mind maps provide students with ASD a predictable and logical structure through hierarchical branching that clearly shows how ideas connect and relate to one another. This visual-spatial approach plays to common strengths among individuals on the spectrum, offering a way to comprehend complex information that might be difficult to process through verbal explanation alone. Concrete illustrations and visual metaphors help make abstract concepts more tangible and understandable. When designed thoughtfully, sensory-friendly mind maps using calm colors, uncluttered layouts, and consistent formatting reduce visual overwhelm and create a comfortable learning environment that supports focus and comprehension.
The Future of Learning Support with Mind Mapping
Mind mapping revolutionizes learning for students with learning disabilities by honoring diverse cognitive styles and reinforcing visual-spatial strengths. It transforms studying into an engaging, empowering process that enhances information access, idea organization, and knowledge retention. Mind mapping is one of the most versatile, accessible, and effective tools for supporting academic success in learners with dyslexia, ADHD, dyscalculia, dysgraphia, ASD, and beyond.
As AI technology continues to evolve, tools like MindMap AI are making this process even easier, allowing students to convert notes, lectures, or PDFs into structured, colorful maps that fit their unique learning styles. The future of education lies in personalization and accessibility, and mind mapping stands at the heart of this transformation. Explore free AI mindmap tools for Learning to experience how technology and creativity come together to support every learner's success.